What Are the 4 Different Types of Blockchain Technology?

Bitcoin was the first blockchain technology, but it has since spawned many others. There are four main types of blockchain technologies in today’s world: public blockchains, private blockchains, consortium blockchains, and hybrid blockchains.
This article will cover each type of blockchain and explain how you can separate the technology for different use cases.
We’ll also cover the pros and cons of each type of blockchains, explore the future of the technology itself and some assumptions of where it might be headed.
What Is Blockchain Technology?
The blockchain was invented in 2008 by Satoshi Nakamoto, who published his white paper describing how he thought the system would work.
Why Is Blockchain Popular?
Blockchain technology has been around for over a decade, but it has only recently become popular due to cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Blockchain technology allows users to create secure decentralized networks where all network participants verify transactions between parties. This eliminates the need for a trusted third party, making it ideal for financial applications.
How Does Blockchain Technology Work?
Blockchain technology works like a distributed ledger system where all transactions are recorded chronologically and publicly available for everyone to view. This makes it impossible to change any transaction once it has been made.
A decentralized network allows users to send money from one account to another without intermediaries such as banks, which means fewer fees and faster transactions.
What Are the Different Types of Blockchain Technology?
The four different types of blockchain technology include public blockchains, private blockchains, consortium blockchains, and hybrid blockchains.
- Public blockchains are decentralized networks where anyone can participate and contribute data and has no centralized authority.
- Private blockchains are centralized systems that allow an authority to access them.
- Consortium blockchains are shared databases that multiple organizations control.
- Hybrid blockchains combine both public and private features that make them unique.
Let’s take a closer look at each type of blockchain technology:
1- Public Blockchains

Public blockchains are a type of blockchain that allows users to create and manage accounts, send and receive payments, and transfer assets. Public blockchains are not controlled by any central authority and are therefore, considered decentralized.
In this permissionless network, everyone has equal rights to participate on the network. Anyone can access it through a web browser. There are no restrictions on what you can do with your own private chain.
One of the first public blockchains released to the public was bitcoin. It enabled anyone connected to the internet to do transactions in a decentralized manner.
The verification process of the transactions is done using consensus methods like proof-of-work, proof-of-stake, and so on. At its core, the participating nodes must do the heavy lifting, including validating transactions.
A public blockchain is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) that allows users to create and maintain a shared record of events across many nodes. Network participants verify the records through consensus mechanisms. Once recorded, the data cannot be altered retroactively.
To know more on the consensus mechanism, please review this article: https://medium.datadriveninvestor.com/how-blockchain-networks-make-decisions-consensus-mechanisms-explained-da463fc4e56a
Advantages
- Public blockchains are decentralized networks that operate independently from any central authority. Any government or company does not control them.
- They are open source, meaning anyone can access and contribute to the code, as therefore <Code-is-Law>. Public blockchains are permissionless, which means anyone can join and participate.
- Public blockchains are distributed, meaning there isn’t a single point of failure. This allows them to scale extremely well and handle massive amounts of transactions.
- Public blockchains provide transparency because all data is publicly available. Anyone can view transaction details, see who owns what, and verify the validity of transactions.
- Public blockchain platforms are immutable, which means once something has been written into the ledger, it cannot be changed.
Disadvantages
- Public blockchains are not private. Anyone can view your transaction history and see who you interacted with.
- Public blockchains are slow compared to private blockchains. Public blockchains are slower because they must publish every transaction they perform.
- Public blockchains are vulnerable to hacking. If someone hacks a public blockchain, they can steal your money and identity.
Use Cases
Public blockchains are often used for cryptocurrency transactions but can be used for many other purposes. For example, they could be used to create a fixed record with an auditable chain of custody, such as a notary service.
Private companies may want to avoid using them because of the public nature of their networks. Instead, they may use a private blockchain solution. Private blockchains are more secure than public blockchains because only authorized parties have access to them.
2- Private Blockchains

Private Blockchains are great when you need to keep your information secure and confidential. They are also great for organizations that want to use them internally.
You can limit access to specific groups of users and give them different permissions. These permissions can range from reading certain transactions to creating new ones.
A private blockchain is also permissioned because it requires users to obtain access before interacting with the network. Permissionless blockchains allow users to participate in transactions, while private blockchains require approval to join them.
Advantages
- Private blockchains are blockchain networks that only allow certain people to access their data.
- This means that no one else can see what transactions occur within the network.
- These blockchains allow you to keep your business information secure from prying eyes.
- Private blockchains are ideal for companies who want to keep their financial dealings private.
Disadvantages
- Private blockchains are not fully decentralized, and there’s always a central authority that controls the network. This makes them less flexible than public blockchains.
- Security risks are higher on private blockchains because if someone gains control over the network, they will be able to change the records or delete them altogether.
Use Cases
There are several different use cases for private blockchains. One example is supply chain management. Companies can use a private blockchain to track assets throughout the supply chain.
Another example is asset ownership; assets can be tracked and proven using a private blockchain. Finally, companies can use a private blockchain for internal voting.
3- Consortium Blockchains

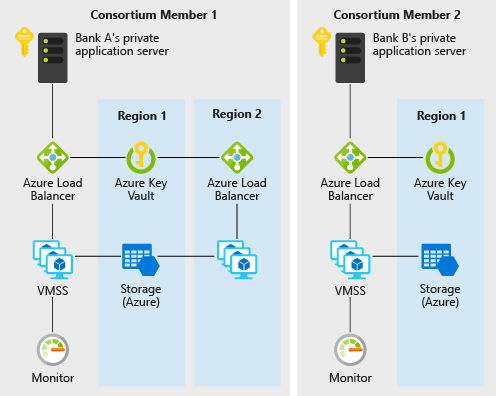
A consortium blockchain is an extension of the public blockchain concept. A consortium blockchain is a distributed ledger technology <DLT> that allows multiple organizations to collaborate on shared databases.
Consortia are usually composed of many organizations, including banks, governments, and other financial institutions. By working together, consortium members can share information about transactions and keep track of assets across various departments within each organization.
As a result, consortiums can provide enhanced security and increased reliability compared to a single entity running its own blockchain. That being said, consortium blockchains are still subject to attacks by malicious actors.
Advantages
- Consortium blockchains are faster because there is no need to wait for every node in the network to validate each transaction on chain.
- They are also more secure because there is less risk of double-spending since only a group of nodes are validating the transactions.
- Consortium blockchains are a type of blockchain network created to solve scalability issues. They are designed to work with many participants at once. This allows them to scale efficiently.
Disadvantages
- Even though they are secure, reliable, and scalable benefits to consortium blockchains, they are still centralized and governed with rules and regulation.
- Less transparency is another downside to consortium blockchains. Each member must agree to follow the same rules when participating in the network.
Use Cases
There are several use cases for consortium blockchains. These include banking and payments, research, and food tracking. However, there are several other use cases. For example, it could be used to create an immutable record of intellectual property rights.
4- Hybrid Blockchains
Hybrid blockchains combine elements from both public and private blockchains. This means they have some characteristics of both a public and a private blockchain.
Hybrid blockchains are a new form of blockchain technology that combines the best aspects of both public and private blockchains.
The main advantage of hybrid blockchains is their ability to offer greater flexibility and efficiency than either public or private blockchains.
This is because they integrate features from both types of blockchains. As a result, they can support all of the benefits of both while minimizing the downsides.
Advantages
- Hybrid blockchain technology combines the best aspects of both public and private blockchains.
- You get all the benefits of decentralization while still having access to centralized control over some elements of your network.
- This type of blockchain solution allows you to take advantage of the security and transparency of a public blockchain while retaining the ability to centralize specific processes within your own organization.
- Organizations can leverage private blockchains’ salient features by leveraging smart contracts, high performance, and complete auditability, while proving transactions on the public blockchain for increased transparency and verifiability.
Disadvantages
- It’s difficult to scale since each chain has its own rules and regulations.
- They are not as efficient as traditional blockchains.
- Hybrid blockchains can reduces the security level in cases of misconfigurations and human error.
Use Cases
There are many different ways that you can use hybrid blockchain technology. One of the most useful ones is for real-estate purposes. You can use the private blockchain to keep all your records securely while making them available to the public.
Hybrid blockchains primarily cater to B2B transactions, so they can be open on the possibility of a decentralized solutions involving B2C (business to customer) use cases, such as ecommerce.
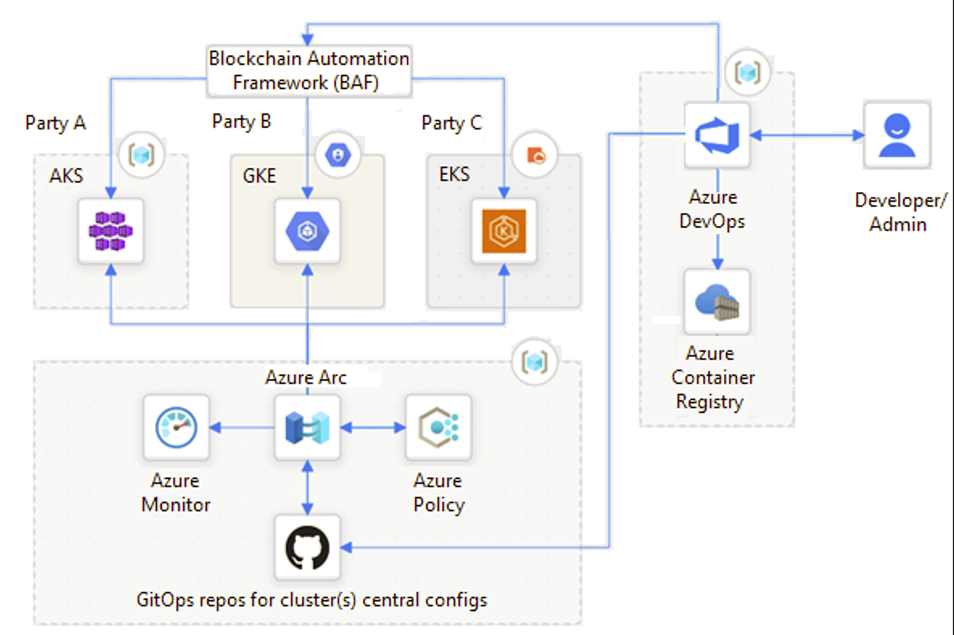
Example of an open-source Blockchain Automation Framework (BAF)
This solution provides a heterogeneous, multi-party, cloud-agnostic DLT network. Parties can host their nodes anywhere and still be part of the network.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is one of the most exciting innovations of our time. It will change how we live, work, and play forever. The different types of blockchains discussed here are the backbone of this revolutionary technology. The technology itself is still young and a early adoption for many. Though, we need to keep in mind that it is already changing the world around us.

